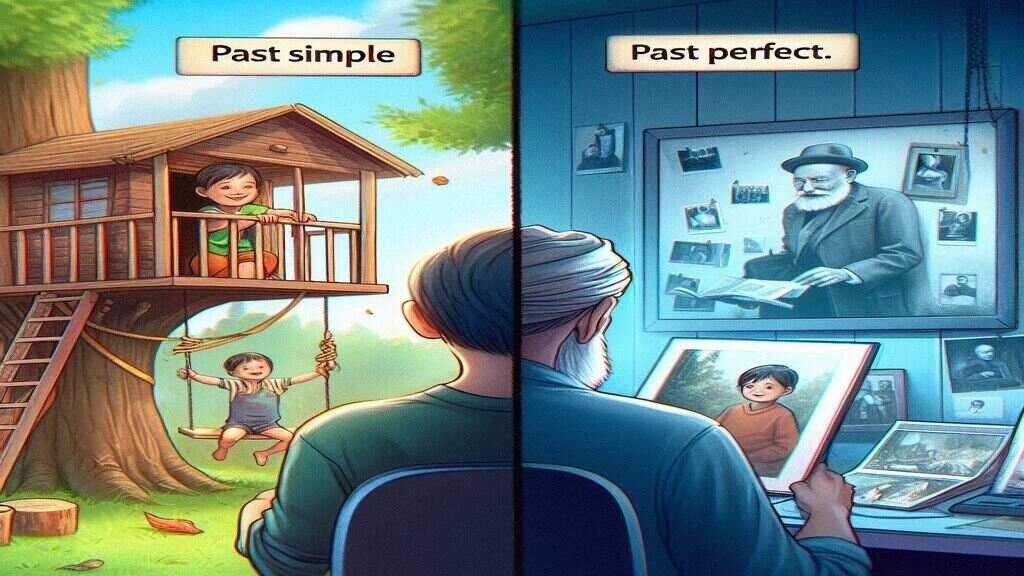
Understanding verb tenses can be tough for kids. But with the right way, even past perfect tense is doable. We use present perfect and past tense to talk about actions finished by now or a certain time before now. By simplifying the grammar rules and showing examples for kids, learning becomes fun and clear for children.
English has three main verb tenses: present, past, and future. The ‘perfect’ tenses (like present perfect) talk about actions done by a certain time before now, or in the future. To make the perfect tense, we use ‘to have’ with the main verb’s past participle.
In Year 2, students learn to write always in the present and past tense. By Year 3, they move to using the present perfect instead of the simple past. By Year 5 and 6, they tackle the present perfect and past perfect tenses, readying for the big tests.
Key Takeaways
- The past perfect tense shows actions finished before another past event.
- Using visual aids and interactive activities helps kids get past perfect tense.
- Using age-appropriate language and being patient are vital when teaching past perfect.
- Doing practice exercises and worksheets helps kids understand past perfect better.
- Talking and doing things that use the past perfect tense daily can make learning it easier.
What is the Past Perfect Tense?
Mastering verb tenses is key in learning English. Today, we’ll focus on the past perfect tense. It’s part of the perfect tense group.
The Three Main Verb Tenses
There are three main verb tenses: present tense, past tense, and future tense. The present tense uses the verb’s base form. For the past tense, we add “-ed” to regular verbs or use irregular forms.
Introducing the Perfect Tenses
Besides these, we have the perfect tenses. The present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect are included. They show completed actions by now, at a point in the past, or a future moment.
Creating these tenses involves using the present/past/future form of ‘have’. Then, add the past participle of the main verb. This mix indicates action completion related to the present, past, or future.
Forming the Past Perfect Tense
The past perfect tense is key in English, showing actions that finished before a certain past point. To form it, we use the past of “have” (had) with a main verb’s past participle. The past participle often ends in “-ed” for regular verbs. Irregular verbs, though, have special past participle forms.
The Structure of Past Perfect
The past perfect formula is simple: had + past participle. This helps us point out an action’s completion before another event in the past. For instance, “I had already eaten dinner by the time you called.”
Examples of Past Perfect in Sentences
Here are a few examples to highlight proper past perfect use:
- “The students had completed their homework before the teacher arrived.”
- “By the time I got home, my husband had made dinner.”
- “After the team had won the championship, they celebrated with their families.”
These examples show how the past perfect tense tells us one past action happened before another. It makes the sequence of events very clear.
How do you explain past perfect to a child?
Teaching past perfect to kids needs a mix of learning methods. Using timelines and visual aids is a great start. It makes the concept clearer to them.
Using Timelines and Visual Aids
Draw a timeline to show events in order. Then, mark when each happened, like in the example. This way, children can see how one event came before the other.
In the example, you’d draw when “my husband had already made dinner” before you arrived home. This helps connect the actions visually for kids.
Comparing Past Events
Comparing events also works well. For instance, saying “By the time I got to the party, my friend had already left.” helps kids see the difference between past and past perfect.
Interactive Activities
Interactive games are perfect for making learning fun. Things like sorting past simple and past perfect sentences or making up their own can really help. Remember, keeping the language simple and examples fitting for their age is crucial.
Contrasting Past Simple and Past Perfect

It’s key for young learners to understand the past simple and past perfect tenses. The past simple talks about actions fully done in the past. The past perfect tells us one past action happened before another past action.
Identifying the Verb Tenses
Teaching how to spot verb tenses in sentences helps kids get the difference between past simple and past perfect. They can figure out which kind of past tense is in a sentence by looking at the words and how they’re used.
Practice Exercises and Worksheets
To master the two verb tenses, kids need practice. Giving them exercises and worksheets with both the past simple and past perfect lets them put their knowledge to the test. It makes learning more hands-on.
| Past Simple | Past Perfect |
|---|---|
| I went to the park yesterday. | By the time I arrived, the others had already started the game. |
| The students finished their homework before the bell rang. | She had prepared a delicious meal by the time I got home. |
| Last year, I visited my grandparents in the summer. | The team had won the championship before the coach retired. |
This table compares the past simple and past perfect tenses visually. It shows how the past perfect is for actions that happened before others in the past. But, the past simple is for actions alone.
Incorporating Past Perfect in Daily Practice
To help children reinforce the concept of the past perfect tense, it’s key to let them practice. This includes using it in everyday talk and writing. When they incorporate the past perfect in sharing past events, it can deepen their grasp of this verb tense.
Age-Appropriate Examples
It’s vital to use age-appropriate examples for children to understand the past perfect tense. For instance, you might tell them, “By the time I got home from school, I had already finished my homework.” Or, ask them, “Had you finished your chores before your friends arrived?” These daily life usage examples make it clear when to use the past perfect in talk and writing.
By using lots of age-appropriate examples and practice, we can help kids get comfortable with the past perfect. This will boost their ability to use the tense in their own day-to-day exchanges and written work.
Conclusion
Explaining the past perfect tense to kids is vital for their language growth. It helps them understand the difference between past perfect and past simple. Activities and examples suitable for their age make learning fun.
Remember: Past perfect is key to talking about past events well. Teaching it well helps students with time, order, and stories. This makes kids better at using English in school and work.
Learning the past perfect tense early is really helpful. Kids who understand it can tell stories and understand others better.
FAQ
What is the Past Perfect Tense?
The past perfect tense shows an action was finished before another past action. You form it with “had” and the past participle of the main verb.
How do you form the Past Perfect Tense?
To make the past perfect, use “had” with the main verb’s past participle. For instance, “I had already eaten dinner by the time you called.”
How do you explain the Past Perfect Tense to a child?
Teaching with a visual timeline is effective. Compare past actions using fun activities to make it clear. Always use examples and words that fit the child’s age.
What’s the difference between Past Simple and Past Perfect?
Past simple talks about completed actions in the past. The past perfect shows one action happened before another. By pointing out different tenses in sentences, students can see the distinction.
How can children practice using the Past Perfect Tense?
Let them use the past perfect when talking about stories or past experiences. Regular practice and fun examples are vital for learning and applying this tense.