An ear infection, also known as otitis media, is a common childhood ailment that can cause discomfort and distress for both children and parents. It occurs when the middle ear becomes inflamed and fluid builds up, leading to a range of symptoms. Being able to recognize the signs of an ear infection in your child is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Key Takeaways:
- Ear infections, also known as otitis media, are common in children.
- Signs of an ear infection in children include ear pain, fever, fussiness, trouble sleeping, and difficulty hearing or responding to sounds.
- Nonverbal cues are important to look for in infants who may not be able to express their pain.
- Early recognition and treatment of ear infections are crucial to prevent complications.
- Consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan for your child’s ear infection.
Recognizing Ear Infection in Toddlers and Infants
Identifying ear infections in toddlers and infants can be challenging, as they may not be able to express their symptoms verbally. However, there are several key signs that parents can watch out for. By paying attention to these cues, parents can recognize and seek timely treatment for ear infections in their young children.
- Tugging or pulling at the ear: If your child is constantly touching or pulling at their ear, it may indicate discomfort or pain in the ear. This is a common sign of an ear infection in children.
- Increased irritability: Ear infections can cause significant discomfort, leading to increased fussiness and irritability in toddlers and infants. They may be more prone to crying or exhibiting signs of general crankiness.
- Trouble sleeping: Ear pain can disrupt a child’s sleep patterns. If your child is having difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or has frequent night awakenings, it could be a symptom of an ear infection.
- Fever: A fever can often accompany an ear infection in young children. It’s important to monitor your child’s temperature and seek medical attention if it rises above the normal range.
- Fluid draining from the ear: In some cases, a child’s ear infection may include fluid drainage from the ear. This may be visible as pus-like discharge or clear fluid.
- Clumsiness or problems with balance: Ear infections can affect a child’s balance and coordination, leading to increased clumsiness or difficulty maintaining equilibrium.
- Difficulty hearing or responding to sounds: If you notice that your child is not responding to sounds as they typically would or seems to have trouble hearing, it could be due to an ear infection.
It is important for parents to be proactive in observing these signs and taking appropriate action. If you suspect your child may have an ear infection, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Identifying ear infections in toddlers and infants is crucial for their well-being. By recognizing the pediatric ear infection signs mentioned above, parents can play an active role in their child’s health and seek timely medical attention when necessary.
Diagnosing and Treating Ear Infections
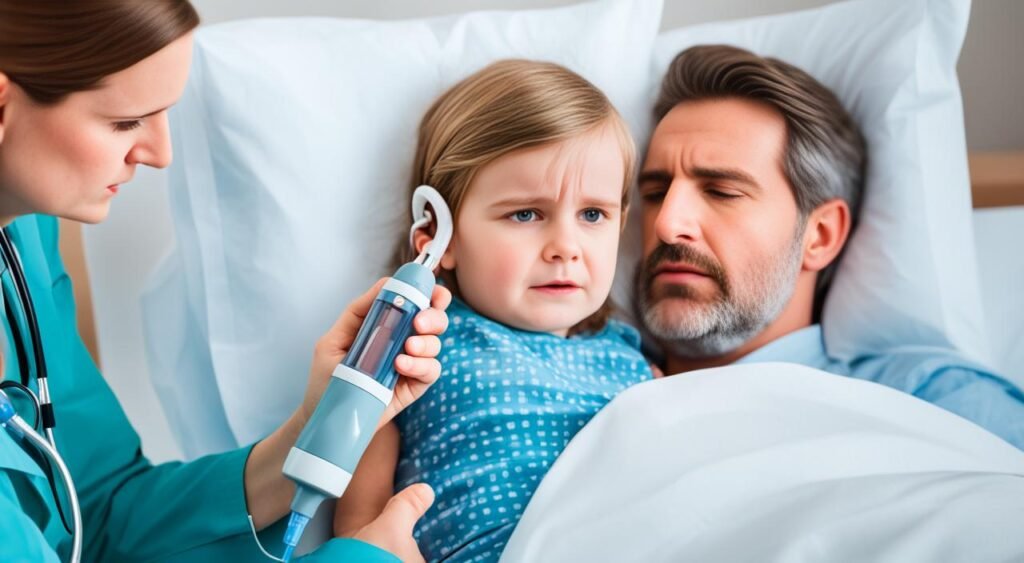

To accurately diagnose an ear infection in children, a doctor will conduct a thorough examination of the child’s ears using a specialized instrument known as an otoscope. This handheld device allows the doctor to visualize the ear canal and eardrum and identify any signs of infection or inflammation.
One common indication of an ear infection is a red and bulging eardrum, which is often accompanied by pain and discomfort. The doctor will carefully examine the eardrum’s appearance and note any abnormalities that may suggest an infection is present.
In some cases, additional tests such as tympanometry may be performed to assess the flexibility of the eardrum and measure the amount of fluid behind it. This test involves placing a small probe in the ear that generates sound and measures the eardrum’s response. It provides valuable information about the middle ear’s function and can aid in diagnosing and monitoring the progress of an ear infection.
Once an ear infection is confirmed, treatment options will be discussed. The approach to treatment often depends on the severity of the infection, the child’s age, and other individual factors.
In many cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help eliminate the infection-causing bacteria. Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can also be recommended to alleviate ear pain and fever. Observation may be advised in mild cases, as some ear infections can resolve on their own without medical intervention. But it’s crucial to closely monitor the symptoms and seek medical attention if they worsen or persist.
For more severe or recurrent infections, the doctor may suggest the placement of ventilation tubes in the eardrums. This minor surgical procedure involves making a small incision in the eardrum and inserting tiny tubes to facilitate better airflow and prevent fluid buildup in the middle ear. Ventilation tubes can be particularly helpful in preventing future episodes of ear infections.
A Comparison of Diagnostics and Treatment Options for Ear Infections
| Diagnostics | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Otoscopy | Antibiotics |
| Tympanometry | Pain relievers |
| Observation | |
| Ventilation tube placement |
The table above provides a summary of the common diagnostic methods and treatment options for ear infections. Otoscopy is a primary diagnostic tool used to directly visualize the eardrum and identify signs of infection. Tympanometry helps assess the ear’s functionality and measure fluid buildup. Treatment options range from antibiotics and pain relievers to observation and, in some cases, surgical intervention with ventilation tube placement.
Preventing Ear Infections in Children
While it may not be possible to completely prevent ear infections in children, certain measures can help reduce the risk.
Vaccination
One of the key steps in preventing ear infections is ensuring that your child is up to date on their vaccinations. Vaccines such as the flu vaccine and pneumococcal vaccine can lower the likelihood of ear infections. Consult with your pediatrician to ensure your child receives the recommended vaccinations.
Hand Hygiene and Environmental Factors
Good hand hygiene plays a crucial role in preventing the spread of germs that can cause ear infections. Encourage your child to regularly wash their hands with soap and water, especially before meals and after using the bathroom. Additionally, taking steps to limit exposure to secondhand smoke, air pollutants, and allergens can help prevent infections. Ensure that your child’s environment is clean and free from potential triggers.
Healthy Feeding Practices
Breastfeeding provides numerous health benefits to infants, including reducing the risk of ear infections. If breastfeeding is not possible, ensure that you bottle-feed your baby in an upright position to minimize the chances of fluid flowing into the middle ear. Avoid bottle-feeding while lying down, as this can increase the risk of infections. Additionally, discouraging pacifier use or thumb sucking can also help reduce the risk of ear infections in infants.
Recommendations for Preventing Ear Infections in Children
| Prevention Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Vaccination | Ensure your child is up to date on recommended vaccines. |
| Hand Hygiene | Promote regular handwashing with soap and water. |
| Environmental Factors | Limit exposure to secondhand smoke, air pollutants, and allergens. |
| Healthy Feeding Practices | Encourage breastfeeding and practice proper bottle-feeding techniques. |
“Preventing ear infections in children involves a combination of vaccination, good hand hygiene, and creating a healthy environment. By following these recommendations, parents can help reduce the risk of ear infections and keep their children healthy.”
Conclusion
Ear infections are a common childhood ailment that can cause discomfort and other symptoms. Recognizing the signs of an ear infection, such as ear pain, fever, and trouble sleeping, is crucial in seeking timely diagnosis and treatment for your child. Consulting a healthcare professional for an accurate assessment and personalized treatment plan is essential.
Prevention is also key in reducing the risk of ear infections in children. By taking preventative measures, such as ensuring your child is up-to-date with vaccinations, practicing good hand hygiene, and limiting exposure to secondhand smoke and allergens, you can help protect your child’s ears from potential infections.
Remember, ear infections can be a source of pain and discomfort for children, but with proper care and attention, their impact can be minimized. Stay vigilant, be proactive, and prioritize your child’s ear health to ensure their overall well-being.
FAQ
What are the signs of an ear infection in children?
The signs of an ear infection in children can include ear pain or discomfort, fever, fussiness, trouble sleeping, fluid draining from the ear, and difficulty hearing or responding to sounds.
How can I recognize an ear infection in toddlers and infants?
In toddlers and infants, signs of an ear infection may include tugging or pulling at the ear, increased irritability, trouble sleeping, fever, fluid draining from the ear, clumsiness or problems with balance, and difficulty hearing or responding to sounds.
How are ear infections diagnosed and treated?
Ear infections are typically diagnosed by a doctor who will examine the child’s ears using an otoscope. Treatment often involves antibiotics, pain relievers, and observation. In some cases, ventilation tubes may be placed in the eardrums to improve airflow and prevent fluid buildup.
How can ear infections be prevented in children?
While it’s not always possible to prevent ear infections, measures such as vaccinating against diseases like the flu and pneumococcal infection, promoting good hand hygiene, limiting exposure to secondhand smoke and pollutants, and avoiding certain feeding practices can help reduce the risk.
Do I need to consult a healthcare professional for my child’s ear infection?
Yes, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan for your child’s ear infection.